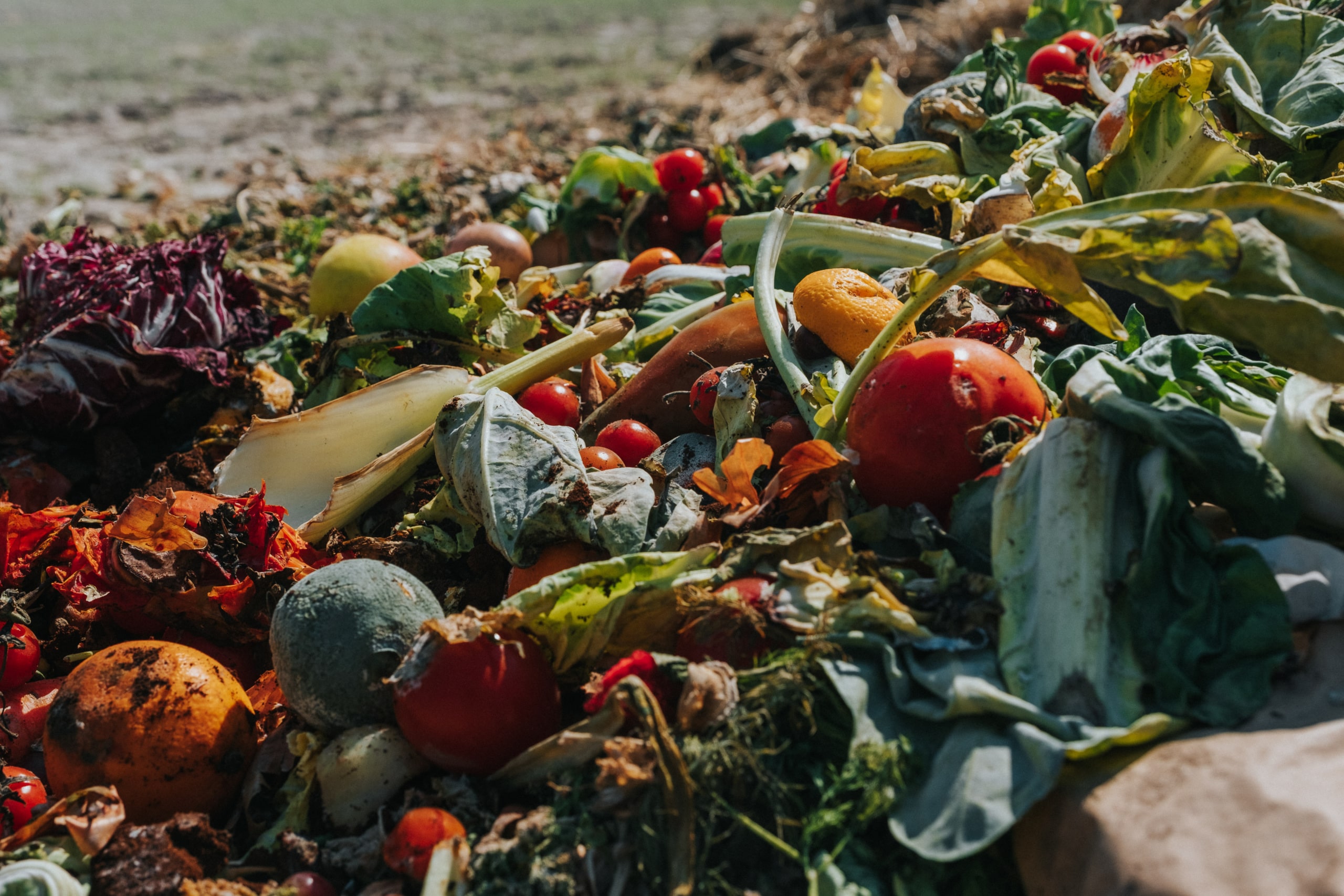
Food waste is a significant problem globally, with approximately one-third of all food produced being lost or wasted each year. This equates to roughly 1.3 billion tons of food that is discarded, while nearly 795 million people around the world suffer from hunger and malnutrition.
Food waste occurs at various stages of the supply chain, from production to distribution and consumption. Some of the factors that contribute to food waste include overproduction, poor storage and transportation, expiration dates, and consumer behavior.
Not only does food waste have severe social implications, but it also has significant environmental and economic consequences. The wasted food ends up in landfills, where it decomposes and releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Moreover, the resources used to produce, transport and process the wasted food, including water, land, energy, and labor, also go to waste.
To combat food waste, individuals, businesses, and governments can take various measures, including reducing overproduction, improving storage and transportation, donating food to charities, composting, and reducing food waste at the household level by planning meals and shopping more efficiently.
Reducing food waste not only helps alleviate food insecurity but also benefits the environment and the economy. By taking simple steps to reduce waste, we can all contribute to building a more sustainable and equitable food system.